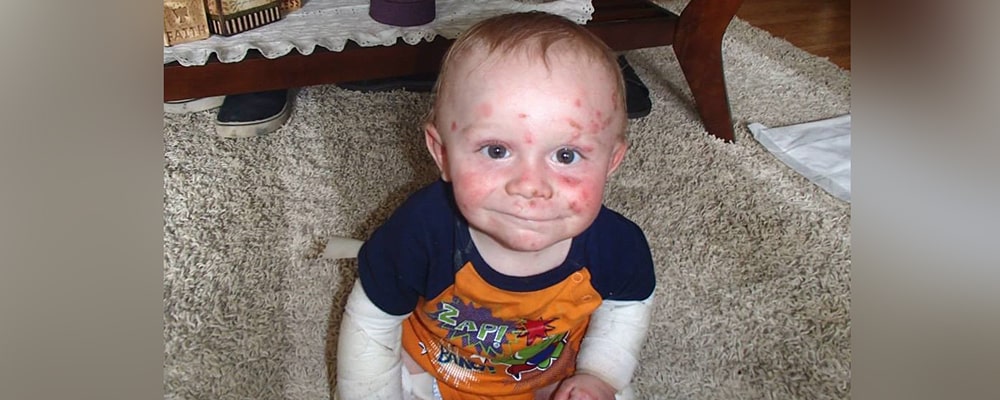
What is EB disease?
Epidermolysis bullosa or EB is a group of skin genetic diseases that cause skin to easily blister and degrades. Those people who are suffering from EB disease, develop blisters and wounds on their skin in response to minor damages or friction, such as rubbing or scratching. EB can be categorized according to the severity and symptoms in individuals, such as its general distribution on patient’s body or whether, along with skin, other parts of the body have been also affected or not. It can also be determined based on correct identification of the protein that exists in patient’s body. This can be achieved based on tests that are run on skin, such as biopsy or genetic testing. Individuals may be affected both in minor or severe kind and face minor discomforts which can be treated by modifications of life style. In some cases, this disease can disable individuals completely and in severe cases cause to death.
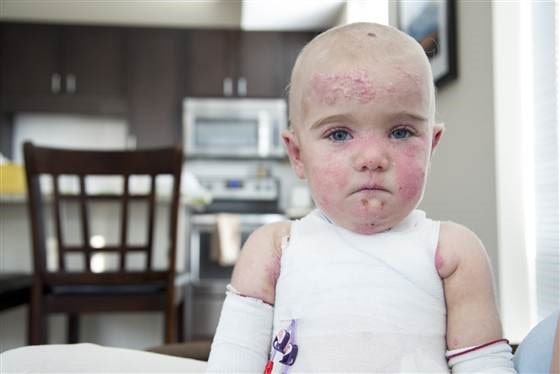
EB can be developed due to changes (mutations) in at least 18 gens which have different roles in maintaining skin’s structure and its integration as well as healing it from damages. This disease can show itself either as predominant or recessive. Therefore, some of the patients may face mild symptoms while others may suffer from more serious and painful symptoms.
Symptoms of EB disease
Symptoms can vary based on its intensity in different individuals:
- Skin becomes brittle and thin, especially in hands and feet area and eventually develops blistered and wounds.
- Thick nails or those that have not been formed completely and naturally
- Blisters inside the mouth and throat
- Development of rigid and thick skin in palm and bottom of the foot
- Hair loss (alopecia)
- Development of white skin bump or mildew
- Dental problems including caries
- Facing difficulties in swallowing food
- Scalp itching and feeling of pain in skin
Treating and managing symptoms of EB disease
To manage and treat the EB disease, usually a team of specialists, who are expert in several fields, is needed. This team should include a dermatologist, a nurse specialist in bandaging wounds, dietician, psychologist and more. Individuals may need consults with different specialists at different stages of their treatment, especially when kids are suffering from this diseases, as they need to receive significant amount of mental treatments and attentions. Managing solutions should vary based on the age, intensity and symptoms of the disease in different people as well as their priorities.
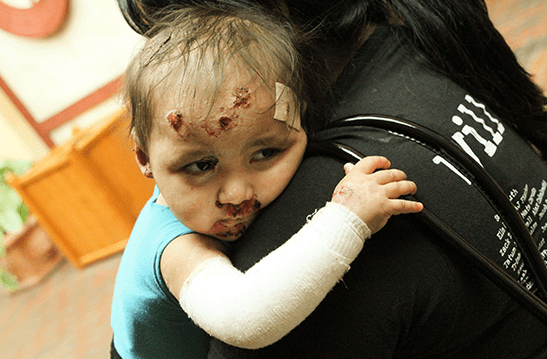
Possible treatments :
Though currently, there is no solid treatment for most of the types of Epidermolysis Bolus (EB), extensive clinical researches on different potential therapies are underway. Gene therapy is believed to be a major contributor to patient improvement. Currently, managing this disease is concluded in supportive actions, such as wound care, pain and infection control, nutrition support and prevention and treatment of further complications. Monitoring imaging tests and studying the test results are also other important steps in helping those individuals who are suffering from the EB disease. However, frequency of these tests may vary due to the intensity of this disease in different individuals.
Conclusion:
Epidermolysis Biolus is a rare disease that can result in fragile and thin skin so that skin can get damaged with minor rubbing or frictions. In severe cases, these symptoms may develop inside the body, such as mouth tissues or stomach as well. The EB diseases is usually an inherited disorder that develops its symptoms mostly during early years of individual’s life .Gene therapy can be a good treatment for this disease, otherwise only supportive actions can be done.








Reviews
Number of pending reviews15232